How To Maintain An Air Compressor

It goes without saying that proper maintenance is key to getting the maximum potential out of your air-powered tools and compressor. Developing (and sticking to) a maintenance routine can save not only time, but also money. That's why our friends at RolAir developed the following air compressor maintenance guide, as originally published on their Zero Sick Days blog.
Keep in mind, RolAir advises that proper safety equipment should always be worn while servicing your air compressor. Do not start, operate or service your machine until you read and fully understand the owner’s manual.
The following chart specifies routine air compressor maintenance procedure, organized by required service intervals.
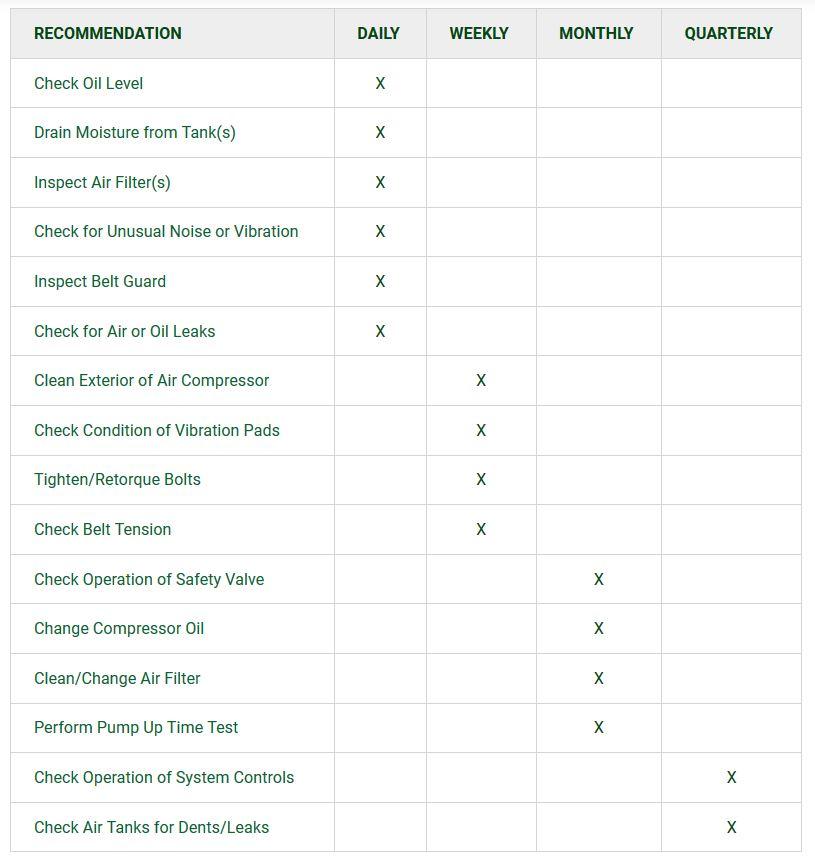
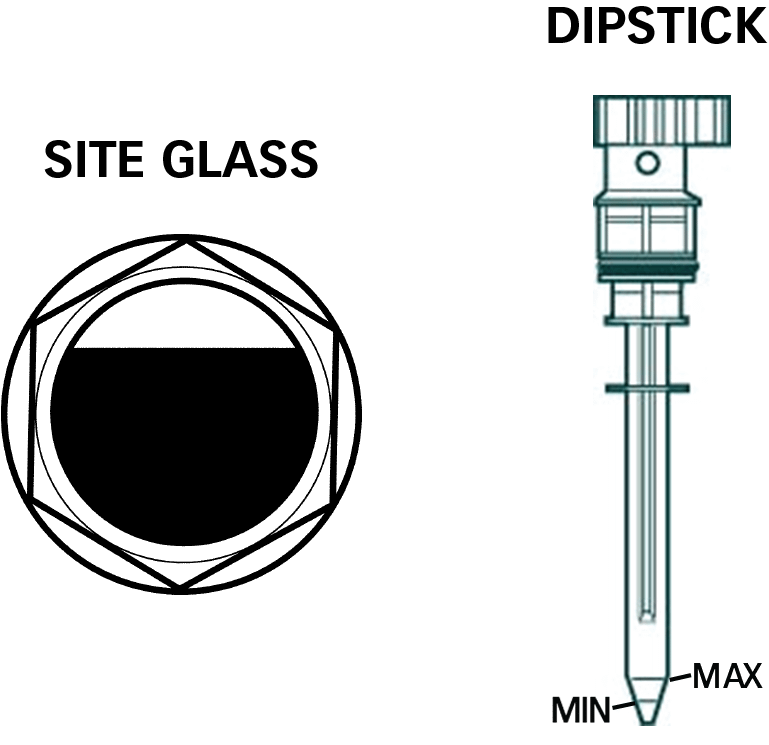
CHECK OIL LEVEL: Recommended service interval - daily.
Prior to daily operation, make a habit of checking the air compressor's oil level for the compressor pump and engine (if compressor is gas-powered). Every direct-drive, hand-carry air compressor has a dipstick to check and maintain the proper oil level. The dipstick also functions as a crankcase vent. NEVER operate a direct-drive unit without the factory-supplied dipstick. RolAir belt-driven air compressors are equipped with a sight gauge to make the task of checking oil levels easier. Always maintain the oil level to read 2/3 full on the sight gauge.
DRAIN MOISTURE FROM TANK: Recommended service interval - daily.
One or more drain valves are installed to allow moisture to be drained on a daily basis from the compressor storage tank(s). Open drains slowly to prevent scale, rust or debris from becoming expelled at a high rate of speed.
INSPECT AIR FILTERS: Recommended service interval - daily.
When checking filters, make sure the filter housing is structurally sound and the element is intact and free of dust and debris. If you need to replace the filter, you can obtain the part number from your owner’s manual.
CHECK FOR UNUSUAL NOISE OR VIBRATION: Recommended service interval - daily.
While the air compressor is running, listen for any rattling or knocking sounds. It is best to perform this step after checking the belt tension, bolts and condition of vibration pads.
INSPECT BELT GUARD: Recommended service interval - daily.
Ensure the belt guard cover is firmly in place and screws are tight. Check for cracks or compromised mounting holes.
CHECK FOR (AIR OR OIL) LEAKS: Recommended service interval - daily.
To check for air leaks, isolate the compressor by removing any air hoses and allowing it to fill up to top pressure. When the compressor shuts off or idles down, observe the tank pressure gauge. Keeping in mind that pressure will drop slightly as the internal air temperature decreases; if the needle drops continuously, a leak is present somewhere in the system. If you can’t locate by sound, coat all fittings in a soap and water solution and watch for bubbling.
To check for oil leaks, watch for pooling oil around the base of the pump and engine (if applicable). Also, if you find yourself having to refill the crankcase frequently, the compressor may be passing an excessive amount of oil. In any case, take the compressor to an authorized service center to diagnose and repair the issue properly.
CLEAN THE AIR COMPRESSOR'S EXTERIOR: Recommended service interval - weekly, as required.
Allow the air compressor to cool to room temperature before attempting to clean. Disconnect electric models from the power source. Wipe down exterior surfaces with a damp cloth. Dry thoroughly prior to operation. DO NOT spray or allow water into motorized components.
CHECK CONDITION OF VIBRATION PADS: Recommended service interval - weekly.
Ensure all vibration pads are in place, and the air compressor sits in a level position. If vibration pads are worn or missing, refer to your owner’s manual for replacement part numbers.
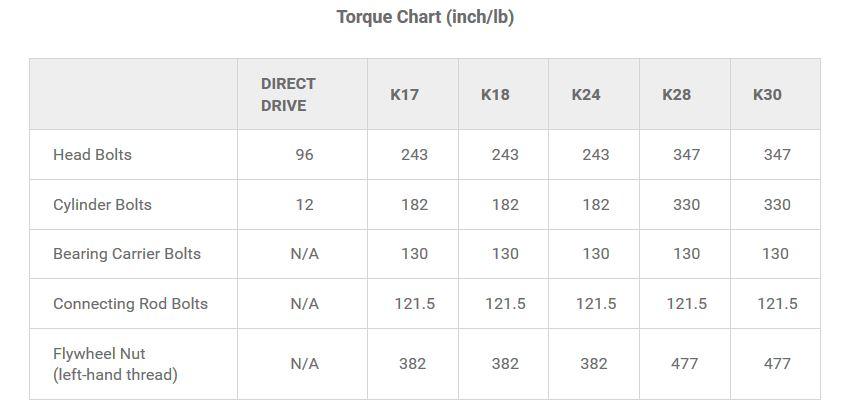
TIGHTEN/RE-TORQUE BOLTS: Recommended service interval - weekly.
Ensure all bolts are tight. With the air compressor at room temperature, re-torque pump bolts according to the specs in the following table:
CHECK BELT TENSION: Recommended service interval - weekly.
Use the diagram below to determine how much deflection is acceptable. If you determine that the belt is loose, obtain a replacement belt or Drive Pulley, and make adjustments as needed. To adjust belt tension, follow these steps:
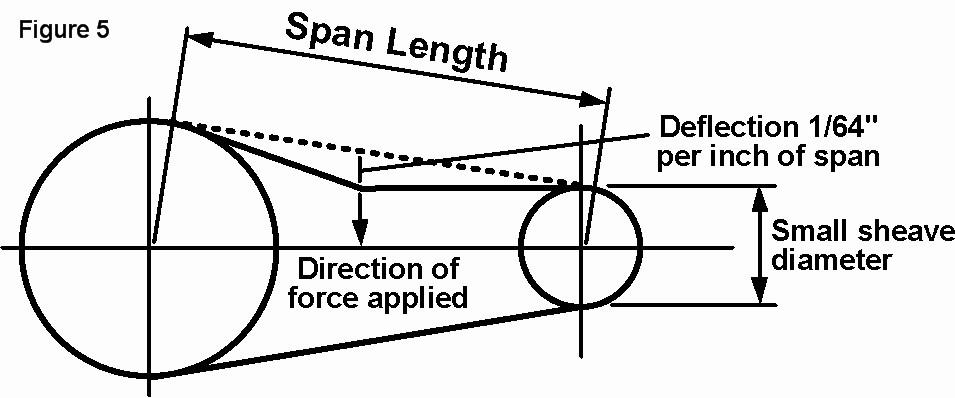
- Roll the belt off the pulley and flywheel.
- Loosen the bolts that hold the motor to the saddle.
- Increase (slightly) the distance between the pump and motor.
- Ensure the pulley and flywheel are properly aligned.
- Tighten the bolts that hold the motor to the saddle.
- Roll the belt onto the pulley and flywheel.
- Check tension. If there’s still deflection, repeat steps 1-7 until proper tension is achieved.
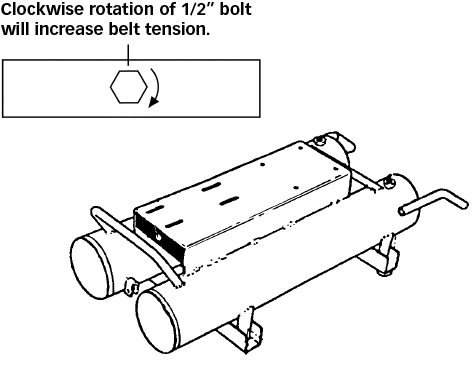
- Loosen the locknuts for engine hold-down bolts; only until the washers below spin freely.
- Rotate the 1/2″ adjusting bolt until desired tension is reached.
- Re-tighten the locknuts to secure the engine.
- Ensure the pulley and flywheel are properly aligned.
CHECK OPERATION OF SAFETY VALVE: Recommended service interval - monthly.
Locate safety relief valve (shown below) and perform a visual inspection. Look for any signs of corrosion or physical damage. With air in the system, slowly and carefully pull the ring to actuate the valve. You should hear a loud hiss of escaping air. If you are unable to open the valve, it will likely need to be replaced.
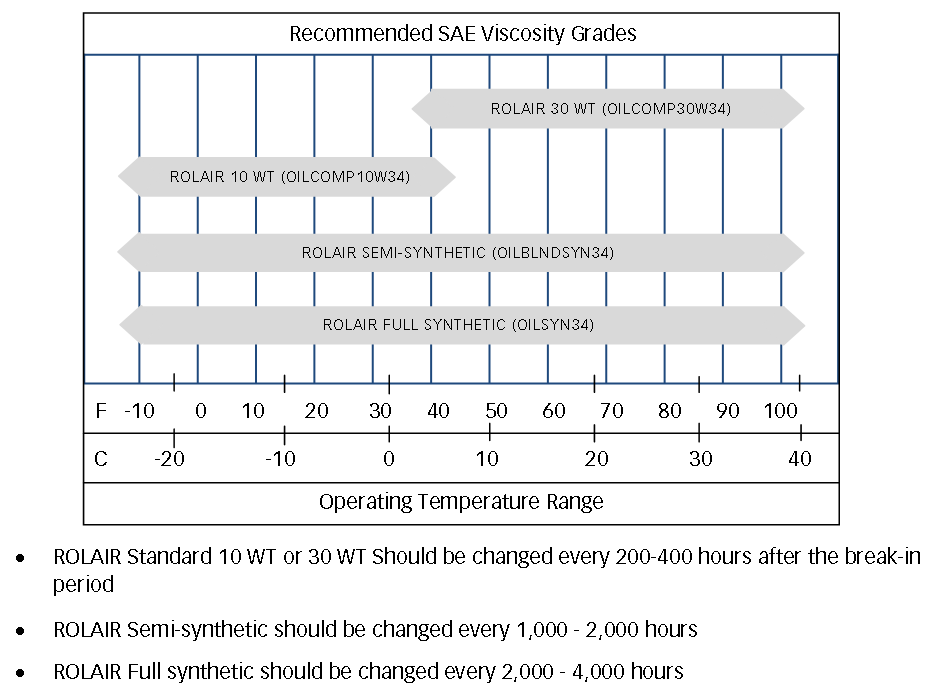
CHANGE COMPRESSOR OIL: Recommended service interval - monthly.
CLEAN/CHANGE AIR FILTER: Recommended service interval - monthly.
Clean air filters using low pressure, compressed air to remove dust and debris. If the filter cannot be cleaned sufficiently, or shows wear, obtain a replacement using the part number in your owner’s manual.
PERFORM PUMP-UP TIME TEST: Recommended service interval - monthly.
With the tank gauge at 0 PSI, and air line(s) disconnected, close drain valve(s) and record the amount of time it takes to build tank pressure. Periodically, test your air compressor against this pump-up time, to determine if it is operating correctly. If the time test is considerably off, contact your local service center to evaluate your compressor.
CHECK OPERATION OF SYSTEM CONTROLS: Recommended service interval - quarterly.
Keeping the process as simple as possible, run the compressor and force it to cycle a few times, by opening the drain valves slightly. While it’s cycling, watch the tank pressure gauge to make sure the needle is rising and falling as pressure increases and decreases.
If it’s an electric model, listen for a brief hiss of air from the pressure switch when the motor shuts off. This signifies that any air caught between the check valve and pump has been evacuated, making for a smooth start-up when the motor kicks back in. The motor will start up again when the tank pressure drops to a certain level, depending on model.
If it’s a gas model, you can expect to hear the engine speed decrease when the compressor has reached its top pressure setting. You’ll also hear air being discharged from the pilot valve. When the tank pressure reaches the lower setting, the pilot valve will activate the throttle control, which increases the engine RPM and starts the cycle over again.
With these tips, and a good understanding of your air compressor, you should be ready for the long-haul.
~ The Nail Gun Depot Team


